Epinephrine
| Epinephrine | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| Item | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Vial | |||||||||||||
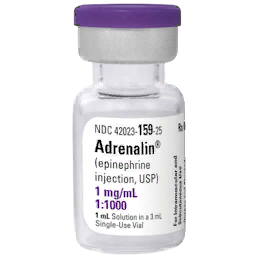
| Vial Size | 1ml | ||||||||||||
| Vial Contents | 1mg | ||||||||||||
| Vial Concentration | 1mg/ml | ||||||||||||
| Medication | |||||||||||||
| Route(s) of administration | IV/IM | ||||||||||||
| Dose Range | 1mg | ||||||||||||
| Medication Effects | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
Epinephrine, or Adrenaline is a medication used to treat cardiac arrest.
Function
Epinephrine is used to improve Return of Spontaneous Circulation in cardiac arrest.
In sinus rhythms it will cause a heart rate and respiration rate increase.
Epinephrine is primarily administered intravenously, with a fast onset, short peak and duration.
Intramuscularly administered epinephrine will have weaker effects and does not have any benefits for ROSC.
Usage
The Use Syringe action is available on the Torso and Limbs in the
![]() Medication
Tab
Medication
Tab
The Push Epinephrine action is available on the Torso and Limbs in the
![]() Medication
Tab
Medication
Tab
Medications require a ![]() Syringe to be able to be drawn and administered.
Syringe to be able to be drawn and administered.
IV access is achieved with IV Catheters or IO devices.
Dosing
Push 1mg IV every 5 minutes during cardiac arrest
Effects
- Heart Rate: + +
- Blood Pressure: + +
- Respiration Rate: + +
Potential Complications
- Tachycardia
- Hypertension
- Cardiac Arrest
Indications
- Cardiac Arrest (PVT/VF/Asystole)
Contraindications
- N/A
 ACM Wiki
ACM Wiki